I. Introduction
The optic nerve serves as a crucial link between our eyes and brain, facilitating the transmission of visual information essential for clear and efficient vision. In today’s digital age, where screen time is prevalent, prioritizing eye health is more important than ever. Maintaining the health of the optic nerve not only prevents vision-related issues but also enhances overall visual performance. Vitamins play a key role in preserving and improving eye health by offering protection against various ailments and optimizing visual functioning.
Incorporating essential vitamins into your diet can have a significant positive impact on eye health. These nutrients are involved in biochemical processes that help maintain the integrity of the optic nerve and other eye components. From reducing oxidative stress to supporting the structural maintenance of eye tissues, vitamins are crucial allies in the journey towards better vision. This article delves into the top vitamins that can boost optic nerve health and enhance vision, providing insights into their benefits, sources, and recommended intake.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is renowned for its pivotal role in supporting healthy vision, particularly in low-light conditions. A deficiency in Vitamin A can lead to night blindness and other vision impairments. Additionally, Vitamin A helps maintain the cornea, the eye’s outer protective layer, ensuring clarity and protection against infections. Moreover, it reduces the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of vision loss.
- Animal-based sources of Vitamin A include liver, fish oils, and dairy products rich in retinol.
- Plant-based sources like carrots, spinach, and sweet potatoes contain beta-carotene, a precursor converted into Vitamin A.
- Recommended daily intake varies by age and gender, with adult men requiring around 900 micrograms (mcg) and adult women needing about 700 mcg for optimal eye health.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C acts as a potent antioxidant that offers numerous benefits for eye health by neutralizing free radicals and combating oxidative stress. It plays a crucial role in collagen production, providing structure to the eye, especially the cornea and sclera. Regular intake of Vitamin C is associated with a reduced risk of cataracts and may slow the progression of age-related macular degeneration.
- Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli are rich sources of Vitamin C.
- The recommended daily intake is 90 mg for adult men and 75 mg for adult women.
- Incorporating Vitamin C-rich foods into your diet can protect your eyes from damage and maintain visual health.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E, another potent antioxidant, plays a critical role in protecting the eyes from oxidative damage. It neutralizes free radicals that can harm eye cells and tissues, including the optic nerve. Studies have shown that Vitamin E can lower the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts, common eye diseases that affect vision with age.
- Nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils, such as almonds, sunflower seeds, and hazelnuts, are rich sources of Vitamin E.
- The recommended daily intake is approximately 15 mg for adults.
- Including these foods in your diet can ensure adequate levels of Vitamin E, protecting your eyes from oxidative stress and supporting long-term eye health.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for maintaining healthy eyes, playing a role in reducing inflammation and supporting immune function in the eyes to prevent eye diseases. Research suggests that Vitamin D may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and dry eye syndrome.
- Sunlight is a primary source of Vitamin D, but dietary sources like fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks can supplement.
- Vitamin D supplements are available for those with limited sun exposure.
- The recommended daily intake ranges from 600-800 International Units (IU) for most adults, depending on individual health needs.
VI. Conclusion
In conclusion, the optic nerve’s health and vision enhancement are paramount, especially in an era marked by increased eye strain. Key vitamins like A, C, E, and D are vital for supporting eye health, preventing damage, reducing the risk of eye diseases, and promoting overall visual well-being. By incorporating foods rich in these vitamins into your daily diet, you can proactively preserve your eye health. Remember, a balanced diet and regular eye check-ups are essential for maintaining optimal vision throughout life.
FAQ
1. What role does Vitamin A play in eye health?
Vitamin A supports healthy vision, particularly in low-light conditions, maintains the cornea, reduces the risk of age-related macular degeneration, and prevents night blindness.
2. How does Vitamin C benefit eye health?
Vitamin C acts as a potent antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals, combating oxidative stress, and reducing the risk of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration.
3. What is the importance of Vitamin E for eye health?
Vitamin E is a potent antioxidant that protects the eyes from oxidative damage, lowers the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts, and supports long-term eye health.
4. How does Vitamin D contribute to maintaining healthy eyes?
Vitamin D reduces inflammation, supports immune function in the eyes, prevents eye diseases like age-related macular degeneration and dry eye syndrome, and is essential for overall eye health.
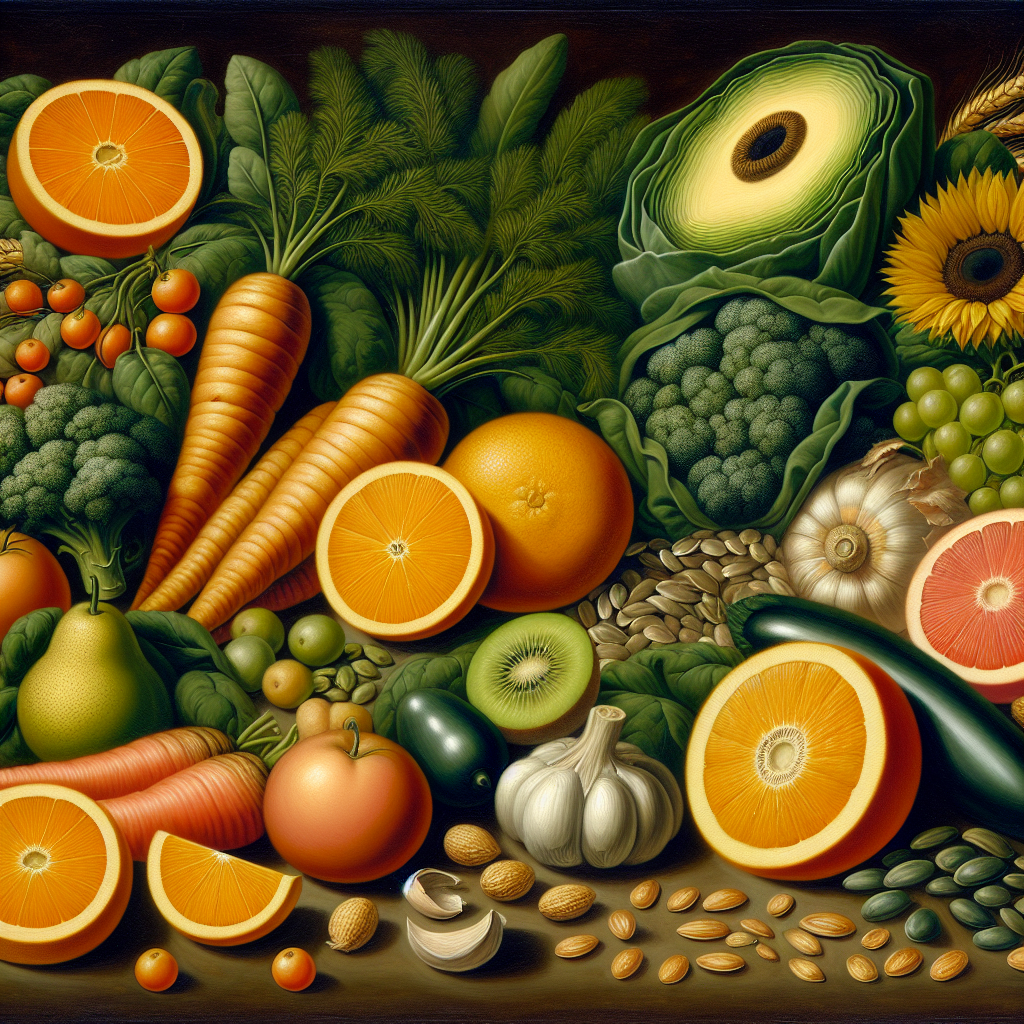










Its interesting to know about vitamins A, C, E, and D that help optic nerve health. Many people don’t realize how much diet affect vision. Eating carrots and citrus fruits could make a big difference! We need more info!